12v led strip lights is low-voltage electricity, and 220V is high-voltage electricity for civilian use. It can also be sai-d that the input voltage is 220V, and the working voltage is 12V.
The 220V light strip is convenient and can be directly connect-ed to the 220V power supply, but it is not safe.
The low-voltage 12v led strip lights is safer. But when connecting, you need to connect a transformer before it can be connect-ed to the power supply.
The 220V light strip plug has a converter with rectifier and constant current output inside. Its rectified and filtered output voltage is 300V DC.
Through constant current conversion, it controls the output current to be tens of milliamperes of DC to drive the LED light strip. The 12V light strip does not have a power converter inside, and 12V DC power is directly input to drive the LED light strip.

LED selection parameters and12v led strip lights direct drive
First of all, let me ask a question, can 12V directly drive a light-emitting diode in series with a resistor?
The maximum operating current of low-power LED lamp beads of various colors is generally 20mA, and the actual value is 5 to 15mA.
For red low-power LEDs, the forward voltage drop is 1.6~2V, green ones are generally 1.8~2.4V, and blue and white ones are 3~3.3V.
Assume that a blue lamp bead is drive-n by a 12V power supply and the operating current is 9mA. Then the current limiting resistor R = (12V-3V)/9mA = 1KΩ. 3V in the formula is the forward voltage drop of the blue lamp bead.
I selected an LED, but still encountered some problems when driving it. The brightness is not as bright as the three-color light, but I only see red.
The parameters are as shown below: the 3535MWAP of Nationstar Optoelectronics was selecte-d.
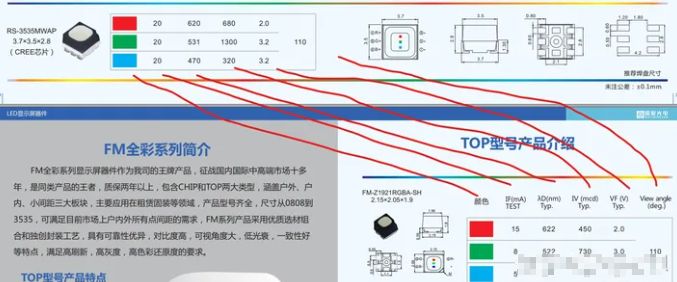
IF: refers to the forward current, which refers to the current when the 12v led strip lights is working. Generally, the working current of ordinary light-emitting diodes is very small, only 10mA-45mA.
When the voltage increases, the current will increase to a great extent, so generally light-emitting diodes are connect-ed in series with protective resistors.
λD: refers to wavelength.
Dies made of different materials can emit different colors.
Even for the same material, different luminescent colors can be obtain-ed by changing the type or concentration of impurities or changing the composition of the material.
The following table shows the luminescent materials used in LEDs of different colors.
Luminous color Material used Wavelength
Ordinary red GaP 700
High Brilliance Red GaAsP 630
Super bright red GaAlAs 660
Super bright red AlGaInP 625-640
Ordinary green GaP 565-572
High Brilliance Green AlGaInP 572
Super bright green InGaNg 505-540
Ordinary yellow GaAsP 590-610
Super bright yellow AlGaInP 590-610
IV: light intensity
The luminous flux emitted by a light source within a unit solid angle is call-ed the light intensity I of the light source.
The unit of luminous intensity is candela (cd), which is commonly use-d millicandela (mcd).
One lumen of light emitted within one unit solid angle is call-ed one candela. Candela is the luminous intensity of a light source in a given direction.
VF: forward voltage
Forward voltage refers to the voltage drop generated between the positive and negative electrodes when the forward current passing through the LED is a specified value, represented by the symbol VF.
The forward voltage of SMD LEDs commonly used by our company is 2.0V-3.5V.
If it exceeds the normal operating voltage, the diode may be broken down. In addition, when the forward voltage is less than a certain value (called the threshold), the current is extremely small and no light is emitted.
When the voltage exceeds a certain value, the forward current increases rapidly with the voltage and emits light.
The measured forward voltage drop is only a few volts, so the light emission is incorrect.
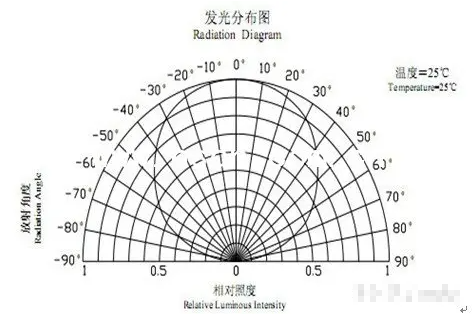
View angle: perspective
In the luminous intensity distribution graph, the angle formed by luminous intensity equal to half of the maximum intensity is called the half value angle.
As shown in Figure <5>.
In the figure, the normal direction of the LED is the direction of the mechanical axis, the direction of the maximum luminous intensity is the direction of the optical axis, and the angle between the mechanical axis and the optical axis becomes the deviation angle.
The thickness of the chip, the overall dimensions of the packaging mold strip, the depth of the bracket reflector cup and the insertion depth of the bracket in the mold cavity all have a direct impact on the half value angle.
During manufacturing, different sizes of half-value angles can be obtain-ed by selecting different materials and selecting different package sizes according to customer requirements.
There are three categories according to the luminous intensity angular distribution diagram:
aHigh directivity, usually with pointed epoxy packaging or metal reflective cavity packaging, without adding scattering agent.
The half-value angle is 5° to 20° or less. It has high directivity and can be use-d as a local lighting source or used in conjunction with a light detector to form an automatic detection system.
b Standard type, usually used as an indicator light, with a half value angle of 20° to 45°.
c scattering type, which is an indicator light with a larger viewing angle, with a half-value angle of 45° to 90° or greater.